[March 2023 update]: Please note that with the rollout of Google Analytics 4, the information in this article is out of date.
Email as an acquisition source has been around since the beginning of the internet. No other method of traffic acquisition is capable of reaching your clients’ prospects so personally at a cost as low as email. For email acquisition to function, all you basically need is a list of emails. With that, you can instantly send promotional material to the inboxes of your clients’ prospects and customers.
Email can be used to promote your client’s products (sales emails, new product emails, etc), engage customers (newsletter emails, birthday emails and similar), or reclaim abandoned carts. Email’s reach is almost complete, with over 3.8 billion email accounts worldwide.
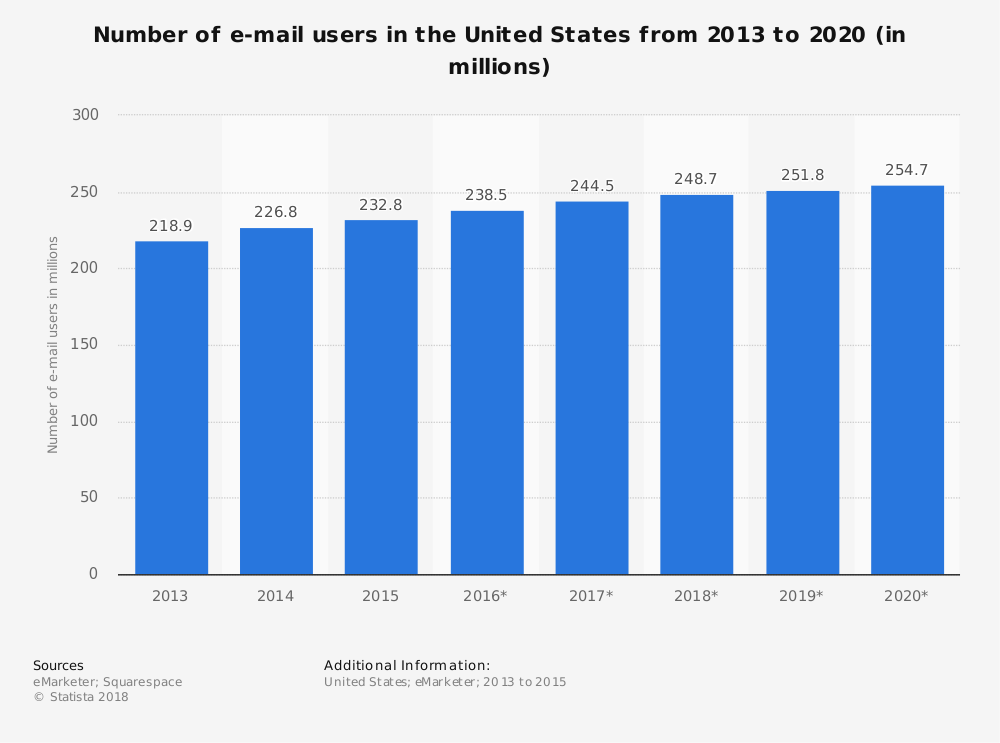
This popularity has made it a very widely used marketing channel with predictable results: inboxes are filled with large numbers of messages from different companies, all attempting to promote their products. This makes it easier for users to miss your promotional emails—especially since people gloss over emails from unfamiliar senders. If you just fire off emails, they will likely be ignored.
There is a way, however, to alleviate this problem. Personalizing your emails—addressing them by name and sending them from known people—helps bring your email up to a 100 percent open rate. In this article, we look at why email personalization is important, how to do it, and how to find further opportunities to improve your email marketing.
Looking instead to improve your one-to-one reach outs to clients? Check out our article on the best business email format to use.
Why email personalization is important
Making emails more relevant to the individual subscriber means adding elements that will make it more personal. If an email contains relevant and beneficial offers for the subscriber, it’s more likely they will open it.
A personalized email tells the recipient that the company is taking care of their needs and knows who they are dealing with. By using the information you know about the prospect in your email, such as their name, location, and the type of products or content they like, you make the email more interesting for recipients, and therefore more worthwhile to open and read.
"A personalized email tells the recipient that the company is taking care of their needs and knows who they are dealing with."
According to research done by Experian, personalized emails have an open rate six times higher than non-personalized emails. And according to research conducted by IDM, personalized emails had an 82 percent increase in open rate and a 56 percent increase in sales.

You might also like: How to Build an Abandoned Cart Email Sequence.
How to personalize emails
Now that we know why email personalization is important, let’s look at how to actually personalize emails. An email can be made more personalized in several ways:
- Subject line personalization
- Email list segmentation
- Personalized content
- Personalized information
- Geolocation and local time
Let’s look at each of these factors.
1. Subject line personalization
Emails that use a prospect’s first name in the subject line or the opening line will instantly feel more personal. While this tactic seems basic, many ecommerce brands neglect to use it.
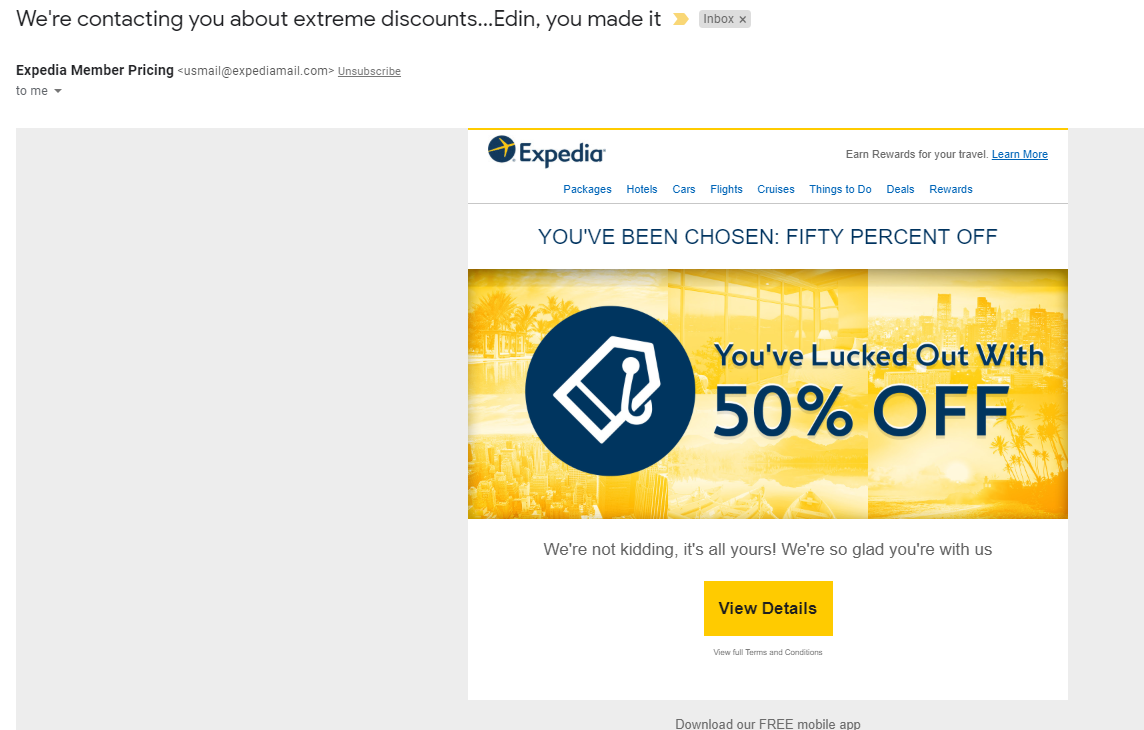
2. Email list segmentation
Email list segmentation is based on a common denominator shared by a group of visitors. A good example is sending a selection of products for men to all the men on your mailing list. This way, you increase the likelihood they will click on products and check your offer.

In addition, a mailing list can be segmented according to the date a prospect joined, or the time from the last purchase, or similar criteria.
3. Personalized content
An email with personalized content provides visitors with information that is relevant to them. To achieve this, you’ll need to collect data about your client’s visitors, and use it to identify the interests, lifestyles, and past behaviors of your mailing list. This way, any email campaigns you create will send content, blog posts, videos, or products that your list is actually interested in seeing.

4. Personalized information
Using data can also help identify a prospect’s personal information. For example, if a store collects data on a customer’s date of birth, this information can be used to send happy birthday emails offering a discount or some other gift.

5. Geolocation and local time
Finally, using a prospect’s geolocation to personalize emails is another tactic a store can use to engage customers. By offering products relevant to a location, the offer can be more impactful to prospects living there, increasing open and click-through rate.
These are some of the ways in which you can personalize your client’s emails. Of course, the more information you have on prospects, the better you can personalize.
Now, let’s see how to collect and use the data to make personalization work better. One of the first places you can begin is your digital analytics, where you can find useful data on your visitor behavior.
Using analytics to find personalization opportunities
Most ecommerce stores use some kind of digital analytics to track the performance of their site. While there are many analytics applications, one of the most popular is Google Analytics, holding approximately 85 percent of the market share. Google Analytics allows you to observe the behavior of your prospects, as well as various demographic data about your visitors. This makes Google Analytics ideal to collect the data necessary to make your personalization effort more effective.
By using different Google Analytics reports, you can analyze various traffic sources, and see how the visitors acquired through these sources interact with your web site. Google Analytics offers features such as segments, which can be readily used to segment your mailing list, and secondary dimensions, which allow you to analyze how two different categories interact. It also allows you to create email campaigns targeted to different groups of visitors (by gender, age, geolocation, etc), and measure the success of those campaigns.
"By using different Google Analytics reports, you can analyze various traffic sources, and see how the visitors acquired through these sources interact with your web site."
The immediate use of analytics for this purpose is to understand the behavior of your client’s customers. When you understand how different groups of customers behave, you will be able to make assumptions about what content will best appeal to them in email.
Google Analytics has four main report sections: audience, acquisition, behavior, and conversions. Each provides insights into different aspects of a website.
Audience reports
The role of the audience report is to provide insight into the visitors of the site. It contains some of the most frequently used ways to segment a mailing list and personalize email campaigns. Here you can find demographic data, types of devices visitors use, their geolocation, and interests.

The demographics report contains data about the visitors’ age and gender. Using this report, you can find out the proportion of male and female visitors.
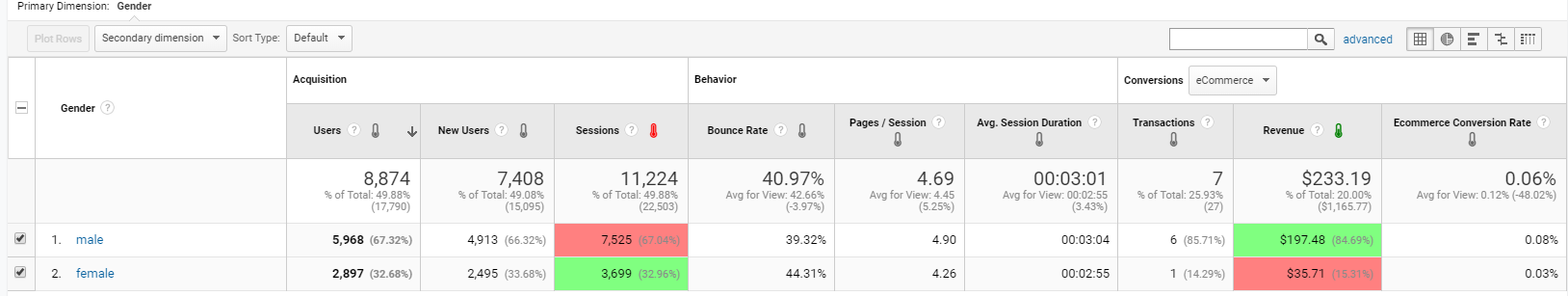
Say you want to run an email campaign. If the target of your campaign is women, you can use information from the above reports to find out what kinds of products and content they particularly like on your client’s site. Knowing this, you can include those things in your emails. For example, you can suggest to your female subscribers the products other women bought or viewed, or promote the blog posts most visited by women. This personalization will help increase open and click-through rates.
This report can be enriched by using a secondary dimension, where you can (if enhanced ecommerce is enabled in your Analytics) use product IDs or landing pages to see which products are more popular or who has made more transactions.
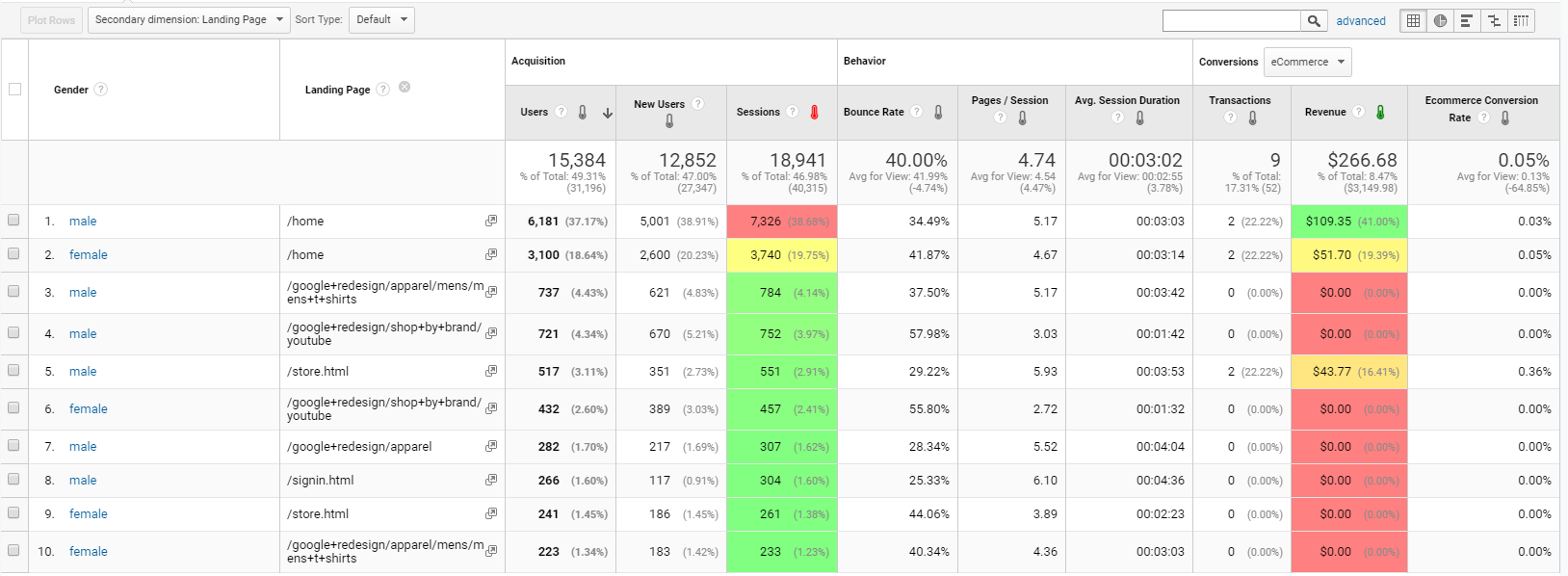
Another useful report is the interests report. Here, you can find visitors’ affinities and in-market segments. Information from these reports can help you find out what your visitors are interested in, so you can target this group with your email campaign.
The affinities report, meanwhile, contains general interests of your client’s customers, such as whether they’re shoppers, travellers, movie lovers, etc. Each of these categories can represent a distinct target for your campaign.
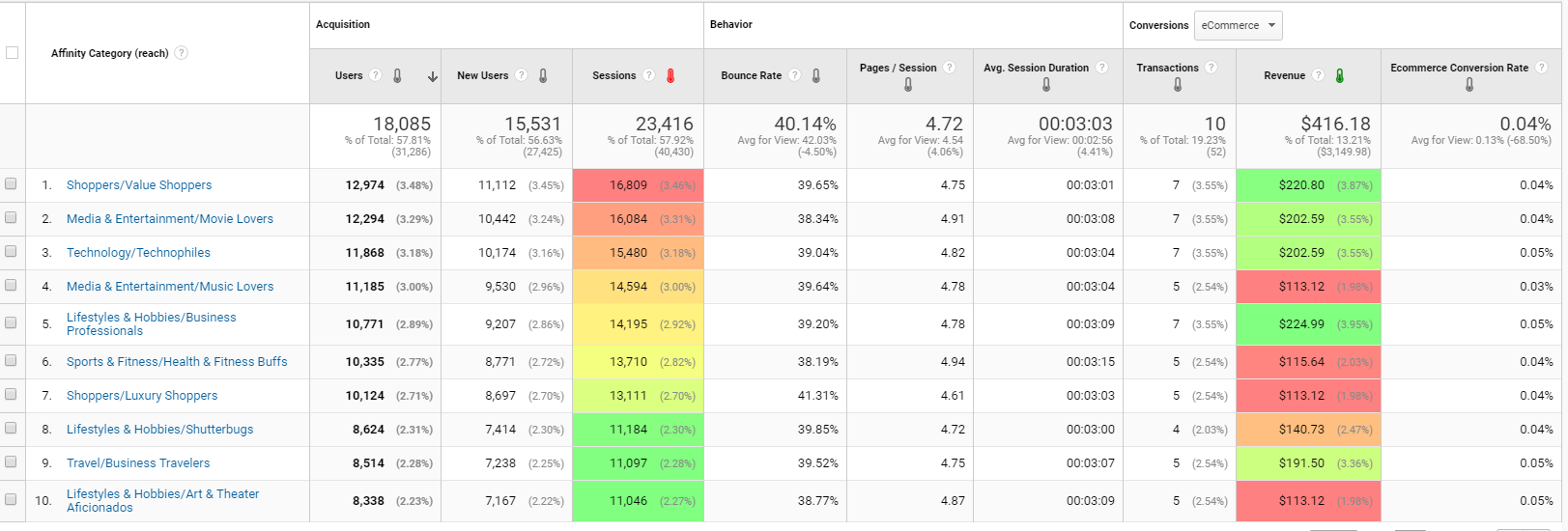
For example, say your client sells cameras. You could use this information to structure an email campaign centered around travel photography to appeal to that interest—helping push both open rates and conversions.
The in-market segments report contains information on what visitors are interested in buying. This report is especially useful, as it provides you with an opportunity to target people with a specific buying intent with a relevant offer.

The in-market segment report can be very useful in providing subscribers with the product they are actually looking to buy. For example, if your client sells household goods such as rugs, you can use the information found here to figure out what people in this segment are looking at most, and send offers for those products directly to them.
By clicking on any of the affinities, you will get the age distribution of each segment. Using this data, you can additionally segment your email campaigns and show appropriate email content to each of these categories. By adding secondary dimensions, you can make the report even more granular and narrow to reflect the group of prospects you are talking to, making your emails more personalized.
Using secondary dimensions
In any report in Google Analytics, you can activate a secondary dimension. A secondary dimension will show you a pivot table where two different categories of report indicators are shown. To activate a secondary dimension, you need to click on the drop-down menu in your report and select one from the list.
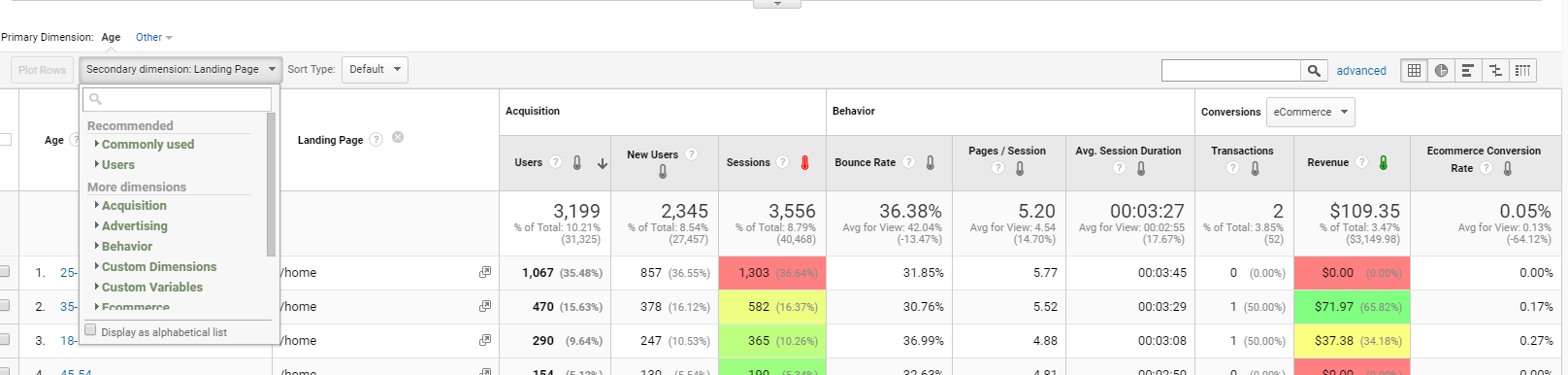
You can pick out landing pages, gender, events by category, and labels (more on this later), and use the secondary dimension to display a more granular report for any primary dimension, such as in-market segment, landing page, acquisition channel, etc.
For products or services that have a significant variation according to a geographical area, you can use the geo report section in the audience report.
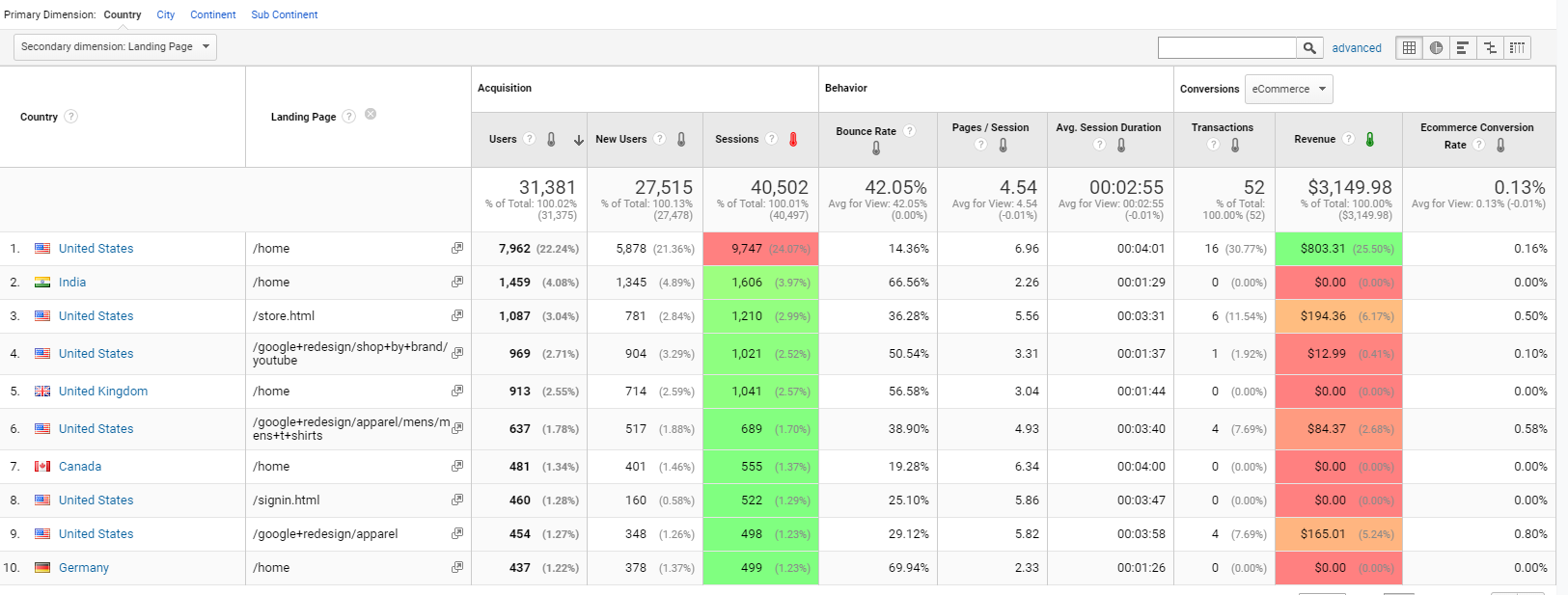
Geolocation can offer you the ability to see what people from different locations prefer, so you can send them offers in your email campaigns that will be interesting only to the visitors from certain locations.
You might also like: Delivering Accessible, Usable, and High-Performance Transactional Emails for Clients.
Acquisition reports
Another section of reports in Google Analytics is the acquisition report. You can use this section to analyze the performance of your email campaigns and compare how each of the different groups of visitors performs.
To increase the personalization of your email campaigns, compare the different campaigns and use secondary dimensions to identify which landing pages have better performance.
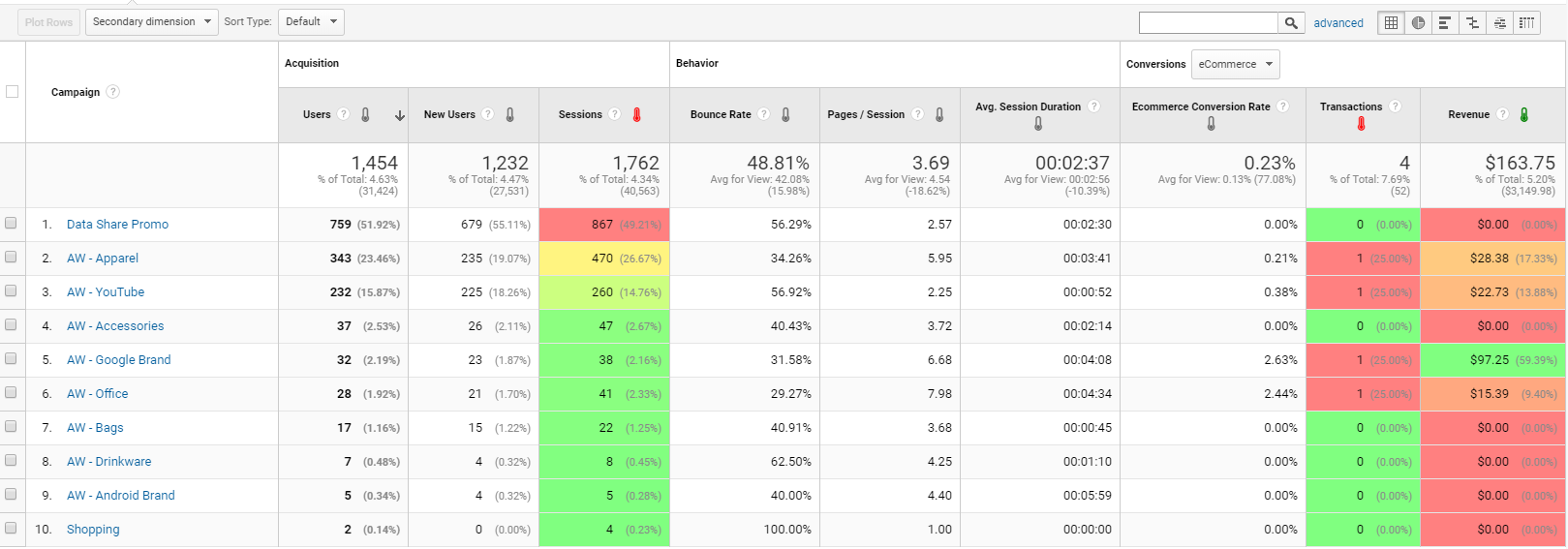
When you find out which of your campaigns have more success with an audience, you can replicate this audience for your email marketing campaign for similar products.
Behavior reports
Behavior reports contain information on how visitors navigate a website, such as what pages they visit, where they landed, and what events they triggered. Visitor behavior can be used to understand what content interests your client’s visitors (such as videos, blog posts, images, or products).
The landing pages report is one of the most important reports of this section. Landing pages that have the most revenue and the highest conversion rate are often prime candidates to use for your campaigns.

When viewing the landing pages report, the homepage will usually be at the top of the list, since many visitors using direct or organic channels to reach the website will land on the home page. However, from a campaign viewpoint, the homepage is not an ideal or representative page. Most campaigns must have a dedicated landing page that you should focus on. Using advanced filters in Google Analytics, you can remove landing pages like the homepage that aren’t relevant to your campaigns.
Events
Google Analytics is able to track events: interactions with the page you can define using tag managing tools. One such tool is Google Tag Manager, which can insert ‘tags,’ pieces of code that send information to Google Analytics, as a visitor interacts with a page element.
Tags can be used to track visitors clicking on links, viewing videos, filling out forms, viewing images, or having social interactions. Within the behavior section, there is an events report subsection. Here you can observe the events triggered by visitors, and once again using secondary dimensions, you can match the events with different groups of visitors.
You might also like: How to Customize Shopify Email Notifications for Clients.
Using segments for personalization
Finally, a feature in Google Analytics that can be most useful for helping personalization is segmenting. Advanced segments make it possible to isolate and identify groups of visitors and observe what they like on the site and what they interact with the most. This feature can be useful to validate your ideas on how to personalize your email campaigns.
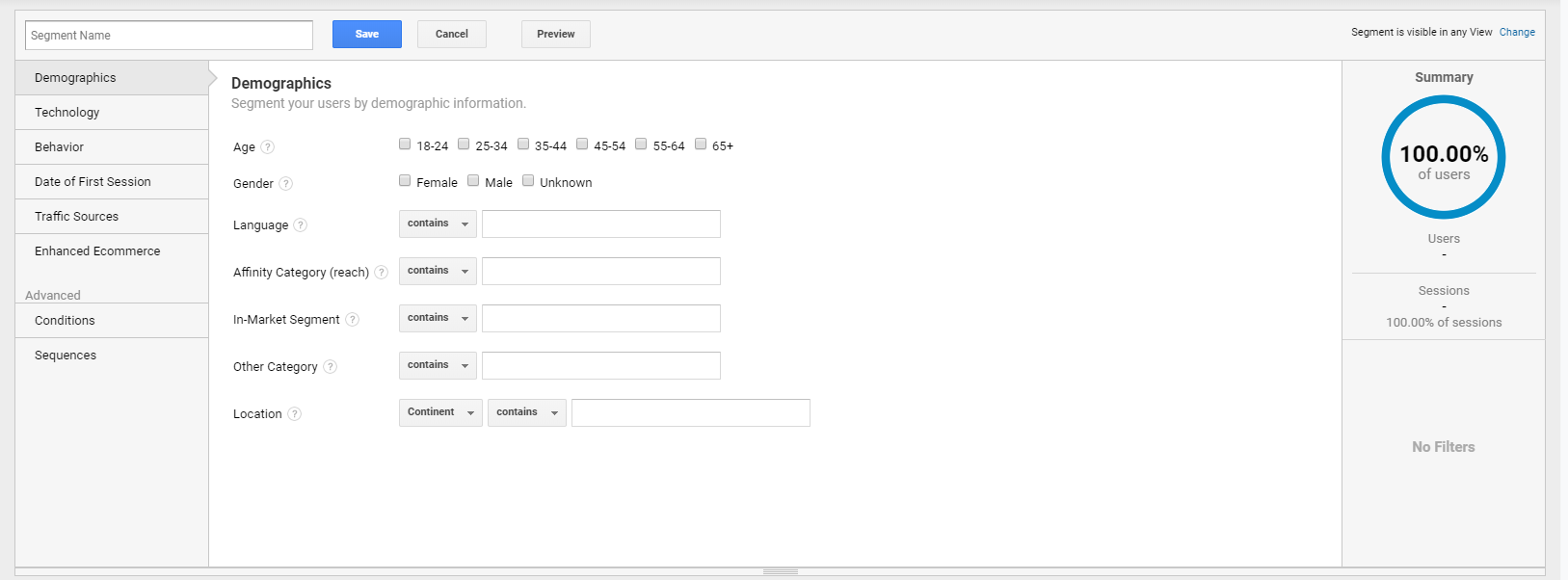
Creating a segment that replicates a target of an email campaign makes it possible to understand what content or offer you can send. For example, if you want to create an email campaign targeted to males between 35 and 44 years old, you can create that segment in Google Analytics.
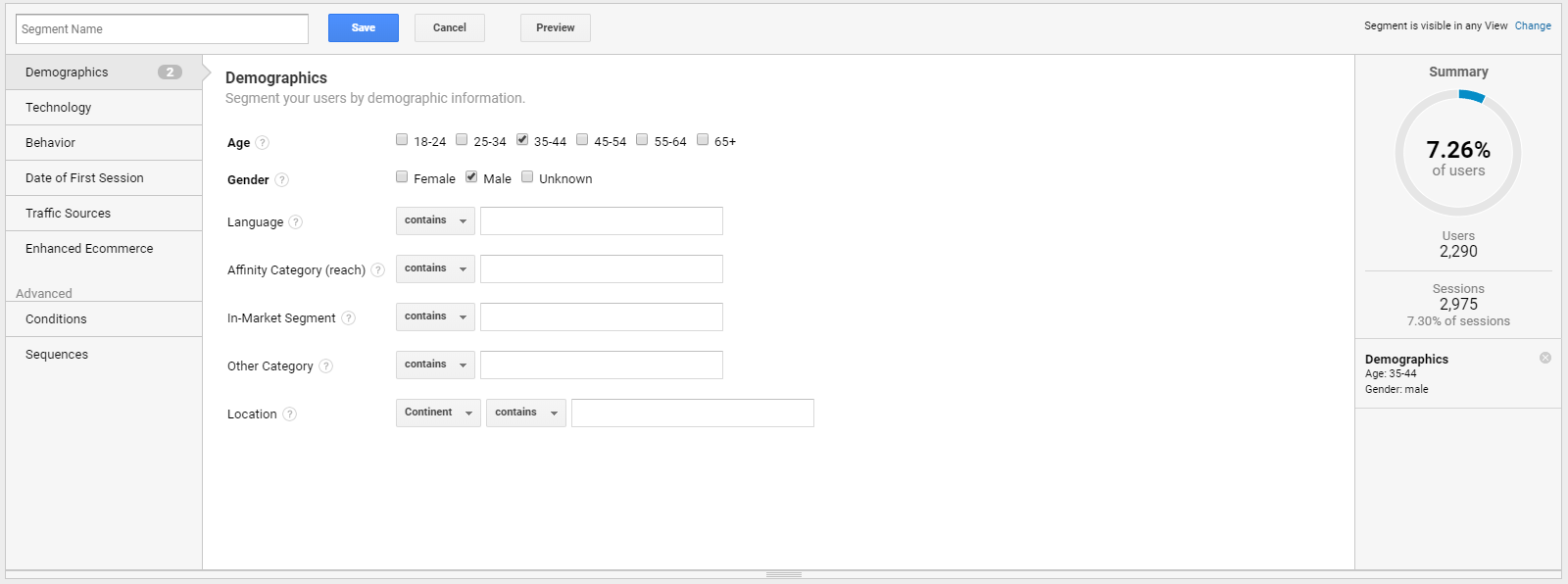
Once you create a segment, you can go through the reports and see what the audience you have created likes and prefers. Checking the landing pages, content pages, products, and events, you can find out how to structure an email campaign that targets this specific group of customers.
For example, if you notice many of your target group viewed a blog post and read it, you can use this blog post to pique the interest of prospects when you send an email campaign. You can also check which products the target group checks the most, and promote these products in a targeted email campaign.
Finally, using segments, you can understand what events, content, and landing pages drive visitor engagement, and use this to devise landing pages for your campaign. Engaging prospects with relevant content makes them more likely to convert and purchase something from your client’s website.
Some caveats on email personalization
Email can be a great acquisition source, as long as you use it judiciously. If your emails are targeted and relevant to the customers, they will be delighted to open and read them as well as to engage with the content you send.
Analytics should be one of the first places you look for personalization opportunities and to send highly engaging emails to your client’s mailing list. No other tactic offers the same kind of insights into the mind of your client’s customers (other than asking them directly).
"Unfortunately, analytics data need to be taken with a grain of salt."
The main issue with using analytics for this purpose is that it is frequently impossible to integrate the data from Google Analytics into email marketing tools. However, most tools contain segmenting features similar to Google Analytics, where you can use the findings you make in Google Analytics to target your campaigns.
Unfortunately, analytics data need to be taken with a grain of salt. The demographic data, which is derived from third party sources, can be inaccurate. Besides, a few useful reports in Google Analytics cannot be segmented, such as goal funnels and user flow reports.
Finally, if your client has a limited number of transactions, you may need to wait long periods of time to gather enough data for this segmentation. Google protects the personal data of visitors, and so limits the ability to glimpse too closely into it, meaning that if you don’t have a lot of traffic to work with, you may not be able to use segments to view transactions or product popularity.
Email personalization for conversion
All of this being said, combining analytics with your marketing campaigns will help you boost open rates and help your clients makes sales. We would like to hear your experiences with using analytics to personalize your email campaigns. What reports do you find useful? Let us know in the comments below.
Read more
- 3 Effective Ways to Help Your Clients Get Their Products Seen and Sold
- Driving Revenue for Your Clients Through Paid Social Funnels
- 10 Tips to Take a Vacation as a Business Owner
- How to Help Your Clients Get Results with Email Marketing
- Scoping is broken. Here’s how one agency fixed it
- How to Save Your Clients Money with Shopify Shipping

